National Education Policy
- National Education Policy, 2020
- Why in News
- Recently, the Union Cabinet has approved the new National Education Policy (NEP),
- 2020 with an aim to introduce several changes in the Indian education system – from the
- school to college level.
- The NEP 2020 aims at making “India a global knowledge superpower”.
- The Cabinet has also approved the renaming of the Ministry of Human Resource
- Development to the Ministry of Education.
- The NEP cleared by the Cabinet is only the third major revamp of the
- the framework of education in India since independence.
- The two earlier education policies were brought in 1968 and 1986.
- Key Points
- School Education:
- Universalization of education from preschool to secondary level with
- 100% Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in school education by 2030.
- To bring 2 crore out-of-school children back into the mainstream through an
- open schooling system.
- 1/6The current 10+2 system is to be replaced by a new 5+3+3+4 curricular
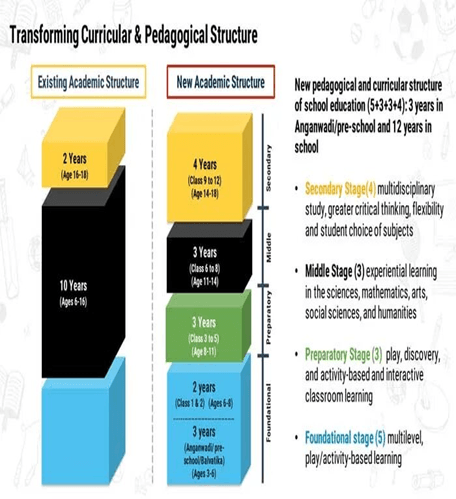
- structure corresponding to ages 3-8, 8-11, 11-14, and 14-18 years #National Education Policy
- respectively.
- It will bring the uncovered age group of 3-6 years under school
- curriculum, which has been recognized globally as the crucial stage for
- development of mental faculties of a child.
- It will also have 12 years of schooling with three years of Anganwadi/ pre
- schooling.
- Class 10 and 12 board examinations to be made easier, to test core
- competencies rather than memorised facts, with all students allowed to take
- the exam twice.
- School governance is set to change, with a new accreditation
- framework and an independent authority to regulate both public and
- private schools.
- Emphasis on Foundational Literacy and Numeracy, no rigid separation
- between academic streams, extracurricular, vocational streams in schools.
- Vocational Education to start from Class 6 with Internships.
- Teaching up to at least Grade 5 to be in mother tongue/regional
- language. No language will be imposed on any student.
- Assessment reforms with 360 degree Holistic Progress Card, tracking
- Student Progress for achieving Learning Outcomes
- 2/6A new and comprehensive National Curriculum Framework for Teacher
- Education (NCFTE) 2021, will be formulated by the National Council for
- Teacher Education (NCTE) in consultation with National Council of
- Educational Research and Training (NCERT).
- By 2030, the minimum degree qualification for teaching will be a 4-year
- integrated B.Ed. degree.
- Higher Education: #National Education Policy

- Gross Enrolment Ratio in higher education to be raised to 50% by 2035.
- Also, 3.5 crore seats to be added in higher education.
- The current Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education is
- 26.3%.
- Holistic Undergraduate education with a flexible curriculum can be of 3 or 4
- years with multiple exit options and appropriate certification within this
- period.
- M.Phil courses will be discontinued and all the courses at undergraduate,
- postgraduate and PhD level will now be interdisciplinary.
- Academic Bank of Credits to be established to facilitate Transfer of Credits.
- Multidisciplinary Education and Research Universities (MERUs), at
- par with IITs, IIMs, to be set up as models of best multidisciplinary education
- of global standards in the country.
- The National Research Foundation will be created as an apex body for
- fostering a strong research culture and building research capacity across higher
- education.
- 3/6Higher Education Commission of India (HECI) will be set up as a
- single umbrella body for the entire higher education, excluding medical
- and legal education. Public and private higher education institutions will be
- governed by the same set of norms for regulation, accreditation and
- academic standards. Also, HECI will be having four independent verticals
- namely,
- National Higher Education Regulatory Council (NHERC) for regulation,
- General Education Council (GEC) for standard setting,
- Higher Education Grants Council (HEGC) for funding,
- National Accreditation Council (NAC) for accreditation.
- Affiliation of colleges is to be phased out in 15 years and a stage-wise
- mechanism to be established for granting graded autonomy to colleges.
- Over a period of time, every college is expected to develop into either an
- autonomous degree-granting College, or a constituent college of a
- university.
4/6Other Changes: #National Education Policy
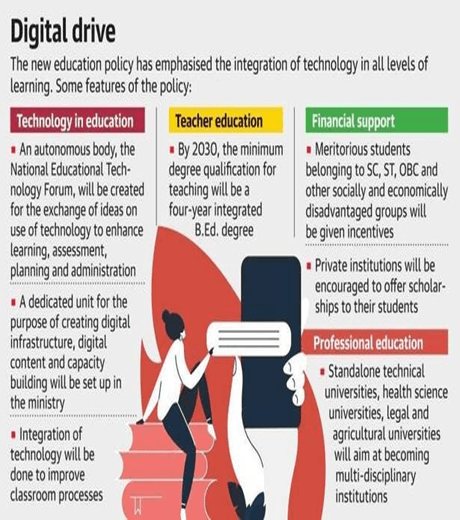
- An autonomous body, the National Educational Technology Forum
- (NETF), will be created to provide a platform for the free exchange of ideas
- on the use of technology to enhance learning, assessment, planning,
- administration.
- National Assessment Centre- ‘PARAKH’ has been created to assess the
- students.
- It also paves the way for foreign universities to set up campuses in India.
- It emphasizes setting up of Gender Inclusion Fund, Special Education
- Zones for disadvantaged regions and groups.
- National Institute for Pali, Persian and Prakrit, Indian Institute of
- Translation and Interpretation to be set up.
- It also aims to increase the public investment in the Education sector to reach
- 6% of GDPat the earliest.
- Currently, India spends around 4.6 % of its total GDP on education.
- Education In India
- 5/6Constitutional Provisions:
- Part IV of Indian Constitution, Article 45 and Article 39 (f) of Directive
- Principles of State Policy (DPSP), has a provision for state-funded as well as
- equitable and accessible education.
- The 42nd Amendment to the Constitution in 1976 moved education from
- the State to the Concurrent List.
- The education policies by the Central government provides a broad
- direction and state governments are expected to follow it. But it is not
- mandatory, for instance Tamil Nadu does not follow the three-language
- formula prescribed by the first education policy in 1968.
- The 86th Amendment in 2002 made education an enforceable right under
#bestndacoaching #topndacoaching #ndacoachinginstitute #National Education Policy #BestNDACoachinginLucknow
Article 21-A.
Related Laws: #National Education Policy
- Right To Education (RTE) Act, 2009 aims to provide primary
- education to all children aged 6 to 14 years and enforces education as a
- Fundamental Right.
- It also mandates 25% reservation for disadvantaged sections of the
- society where disadvantaged groups
- Government Initiatives:
- Way Forward
- A New Education Policy aims to facilitate an inclusive, participatory and
- holistic approach, which takes into consideration field experiences, empirical
- research, stakeholder feedback, as well as lessons learned from best practices.
- It is a progressive shift towards a more scientific approach to education. The
- prescribed structure will help to cater the ability of the child – stages of cognitive
- development as well as social and physical awareness. If implemented in its true
- vision, the new structure can bring India at par with the leading countries of the
- world.
